Types of Organic Reactions and Their Mechanism
Types of Organic Reactions and Their Mechanism: Overview
The topic covers the fission of a covalent bond, substrate and reagent. It explains the electron movement in organic reactions, resonance structure and hyperconjugation. It also explains the electromeric effect and the types of organic reactions.
Important Questions on Types of Organic Reactions and Their Mechanism
Which one of the following carbonyl compound when treated with dilute acid forms the more stable carbocation?
Write correct order of stability of following carbocations :
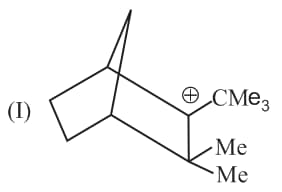
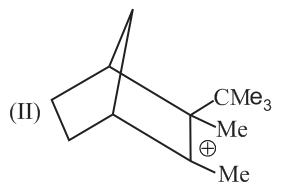
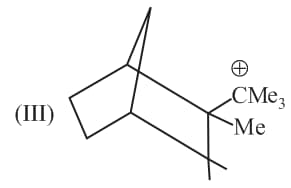
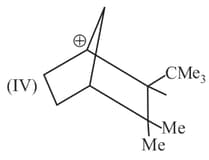
Rank the following free radicals in order of decreasing stability:
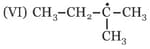
and reactions differ from each other because of:
The reaction of –
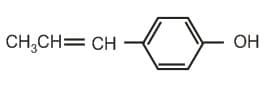
with HBr gives
The correct stability order for the following species is
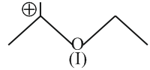
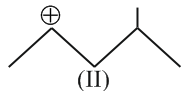
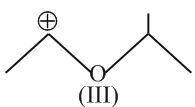
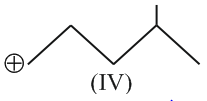
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds.
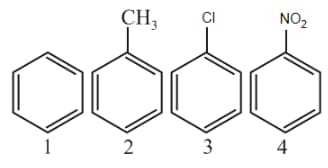
Which of the following has the highest nucleophilicity?
Assertion. Tertiary carbocations are generally formed more easily than primary carbocations.
Reason. Hyperconjugation as well as inductive effect due to additional alkyl groups stabilise tertiary carbocations.
Define intramolecular elimination reactions.
What is elimination reaction?
Why reactions are stereoselective?
Define stereospecificity of an organic reaction.
Define stereoselectivity of an organic reaction.
Define Regioselectivity of an organic reaction.
Define Regiospecificity of an organic reaction.
What are trans and syn addition?
Write an example of an aromatic unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Write the hydrolysis reaction of acyl chlorides.
What is allylic nucleophilic substitution reaction.
